Introduction
Adding a primary key to an existing table in PostgreSQL is a task that database administrators and developers perform to ensure data integrity and optimize database performance. This tutorial will guide you through the steps to add a primary key to an existing table in PostgreSQL, explaining the necessary SQL commands and considerations.
Prerequisites
- Access to a PostgreSQL database
- Sufficient privileges to modify table structures
- Basic understanding of SQL and database concepts
Understanding Primary Keys
A primary key is a column or a group of columns used to uniquely identify each row in a table. It must contain unique values and cannot contain NULL values. A table can have only one primary key.
Step 1: Verify the Current Table Structure
Before adding a primary key, check the existing table structure to confirm there isn’t already one and to decide which column(s) could serve as the key.
You can do this in two ways — from the command line or visually in Beekeeper Studio.
Option 1 — Using psql
-- Replace 'your_table' with your table name
\d your_table
This displays the table’s columns, indexes, and constraints directly in psql.
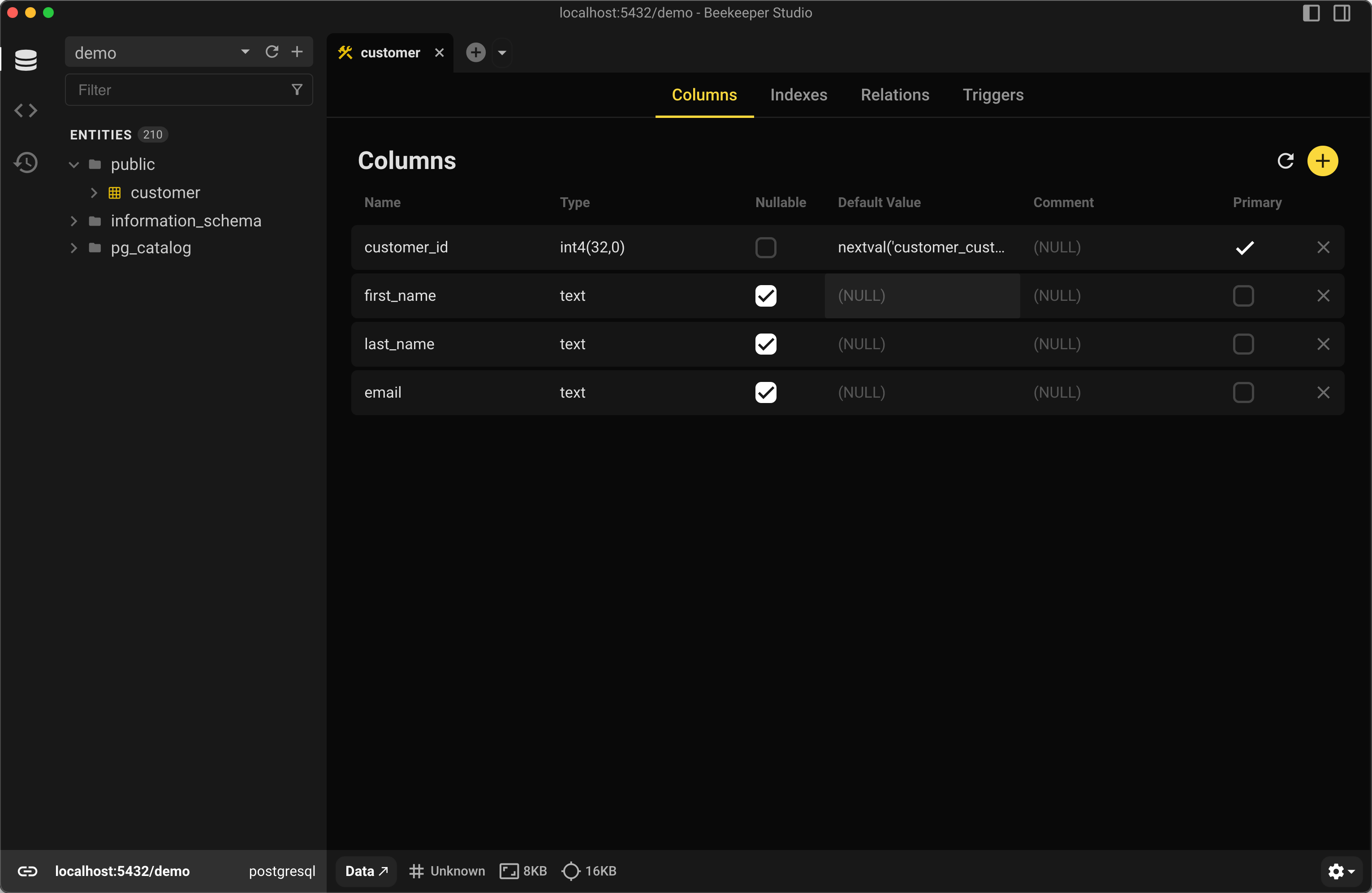
Option 2 — Using Beekeeper Studio
Right-click your table in Beekeeper Studio and select View Structure to see all columns, indexes, and constraints visually.
Step 2: Choose the Appropriate Column
Choose a column that is guaranteed to be unique for each row. If such a column does not exist, you may need to create a new column or use a combination of columns to form a composite key.
Step 3: Add a Primary Key
Single Column Primary Key
If you decide on a single column that uniquely identifies each row, assuming you are connected to the correct database, you can use the following SQL syntax:
-- Replace 'your_table' and 'column_name' with your actual table name and column name
ALTER TABLE your_table
ADD PRIMARY KEY (column_name);
For example, if you want to add a primary key to a table named customer that has columns named customer_id, first_name, and last_name, you could use the following ALTER TABLE command:
ALTER TABLE customer ADD PRIMARY KEY (customer_id);
This would create a primary key on the customer_id column.
Adding a Composite Primary Key to an Existing Table
Alternatively, you could create a composite primary key that consists of multiple columns, like this:
ALTER TABLE customer ADD PRIMARY KEY (first_name, last_name);
This would create a primary key that consists of both the first_name and last_name columns.
Step 4: Verify the New Primary Key
After adding the primary key, it’s important to verify that it has been correctly applied to the table.
-- Check the constraints on the table to confirm the primary key exists
SELECT conname, contype
FROM pg_constraint
WHERE conrelid = 'your_table'::regclass;
If you prefer using a GUI, Beekeeper Studio automatically displays a key icon next to the primary column in the Structure tab once the constraint is added.
Expected Output using customer
conname | contype
------------------------------+---------
customer_pkey | p
customer_support_rep_id_fkey | f
contype p indicates a primary key constraint.
Considerations When Adding a Primary Key
- Data Uniqueness: Ensure the column(s) you are making a primary key have unique data for all rows.
- Performance: Adding a primary key on large tables can be resource-intensive and time-consuming. Consider maintenance windows for large tables.
- Data Integrity: Once a primary key constraint is added, any insert or update operation that attempts to introduce duplicate entries will result in an error.
Summary
Adding a primary key to an existing table in PostgreSQL helps maintain data integrity and improve performance.
Whether you prefer command-line SQL or a visual workflow, tools like Beekeeper Studio make it easy to inspect your schema, verify new constraints, and avoid mistakes.
Need to verify your SQL syntax before executing? Try our free SQL Syntax Checker — and once you’re ready to apply changes, open your database in Beekeeper Studio to see the results instantly.
 Beekeeper Studio Is A Free & Open Source Database GUI
Beekeeper Studio Is A Free & Open Source Database GUI
Best SQL query & editor tool I have ever used. It provides everything I need to manage my database. - ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Mit
Beekeeper Studio is fast, intuitive, and easy to use. Beekeeper supports loads of databases, and works great on Windows, Mac and Linux.
What Users Say About Beekeeper Studio
"Beekeeper Studio completely replaced my old SQL workflow. It's fast, intuitive, and makes database work enjoyable again."
"I've tried many database GUIs, but Beekeeper strikes the perfect balance between features and simplicity. It just works."
